So, you’ve decided to embark on the exciting journey of learning to play the guitar! Whether you’re drawn to melodies, rhythmic strumming, fingerpicking patterns, soaring solos, catchy riffs or the ability to express yourself through music, this guide will provide you with the essential information to get started.
Choosing the Right Guitar
The first step is to select the right guitar for your needs. While there are many types of guitars available, the most common for beginners are:
- Acoustic Guitar: This is a popular choice for its versatility and ability to produce a rich, warm sound. An acoustic guitar doesn’t need to be plugged in. They are transportable and light so you can put it in its case and take it with you. They come in different body sizes so you can find one that fits you perfectly.
- Electric Guitar: Ideal for playing rock, blues, and other genres, electric guitars offer a wider range of tones and effects. If you like gear and volume and bands there’s lots to play with.
- Classical Guitar: With nylon strings and a wider neck, classical guitars are often used for classical music and fingerstyle playing. Often these are great for beginners due to the nylon strings being a bit easier to press down.
Consider your budget, playing style (or what motivated you to play guitar) and physical comfort when making your decision. You can often find excellent quality second hand guitars so maybe consider this while you’re finding your feet.
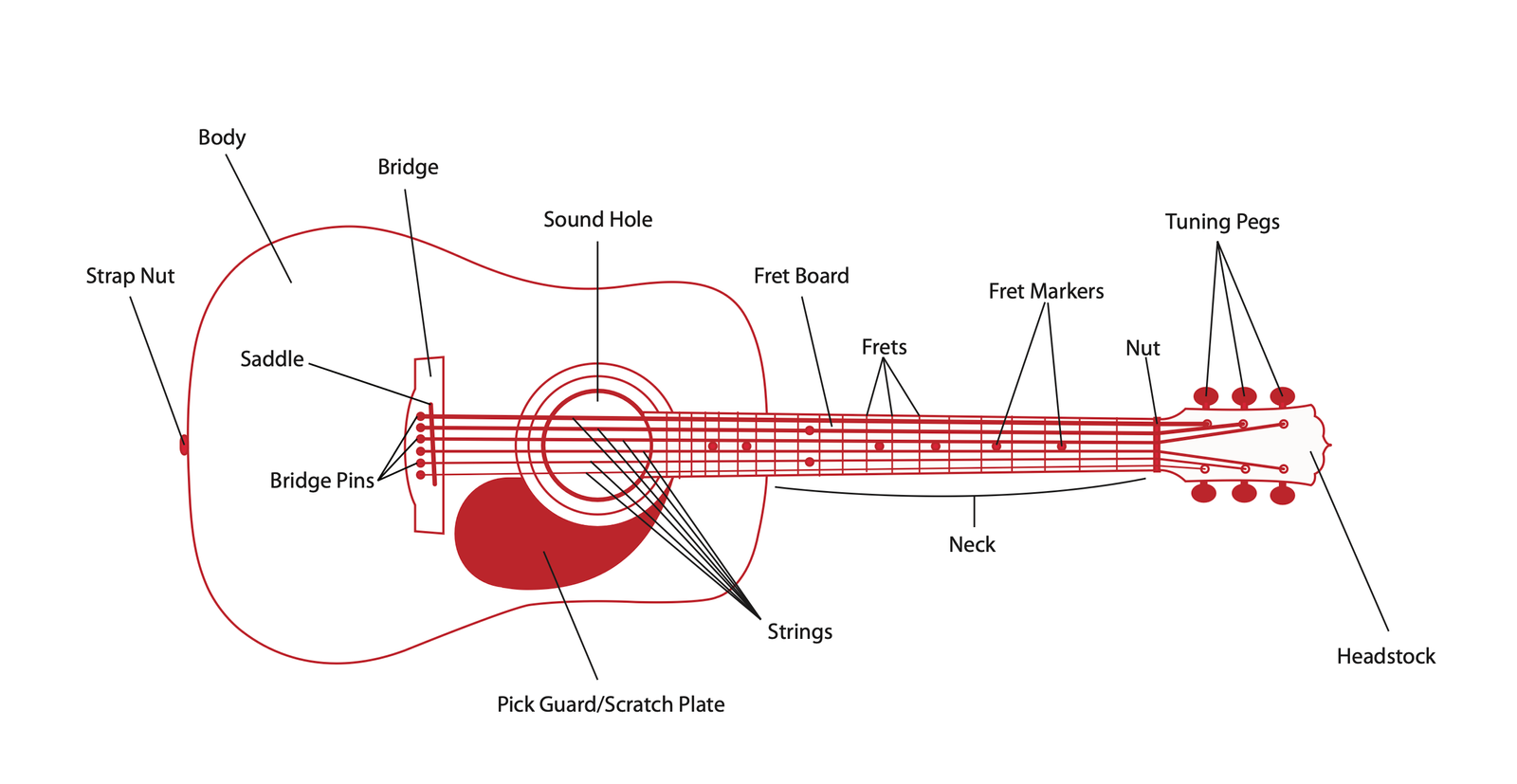
Essential Guitar Parts
Familiarise yourself with the basic parts of a guitar:
- Headstock: The part at the end of the neck where the tuning machines are located.
- Neck: The long, slender piece that connects the headstock to the body.
- Fretboard: The wooden face on the front of the neck that houses the frets.
- Frets: The thin metal wires on the neck that determine the pitch when a string is pressed down.
- Body: The main rounded part of the guitar that amplifies the sound.
- Strings: The six strings that run from the headstock to the bridge.
Holding the Guitar
Correct posture is crucial for playing comfortably and avoiding injuries. Here’s a basic guide:
- Sitting: Sit upright with your feet flat on the floor. Avoid hunching over for too long with your back. If you’re playing for a while, take time to stand and stretch. It can be helpful to raise your right knee with a step (or left if you’re left handed). Sometimes it’s helpful to wear the guitar on its strap when you’re sitting so you can hold it at a height that is comfortable for your hand and wrist position. You’ll also notice that once you go from sitting like this to standing your guitar will remain in the same position.
- Standing: Keep your feet shoulder-width apart and your back straight.
- Guitar Placement: Rest the guitar on your right thigh (if you’re right-handed) or left thigh (if you’re left-handed). To raise the guitar into a comfortable position for your hands use a step for your foot. Make sure the neck of the guitar isn’t too low, this will avoid overbending of your wrist (fretting hand) and enable you to position chord shapes easier.
Tuning Your Guitar
A well-tuned guitar is essential for producing accurate sounds. You can use a tuning fork, a tuner app, tuner stomp box or even your ear to tune your guitar.
There are many free tuning apps available these days that are visually very easy to use. Start there. You will need to know the names of the guitar strings.
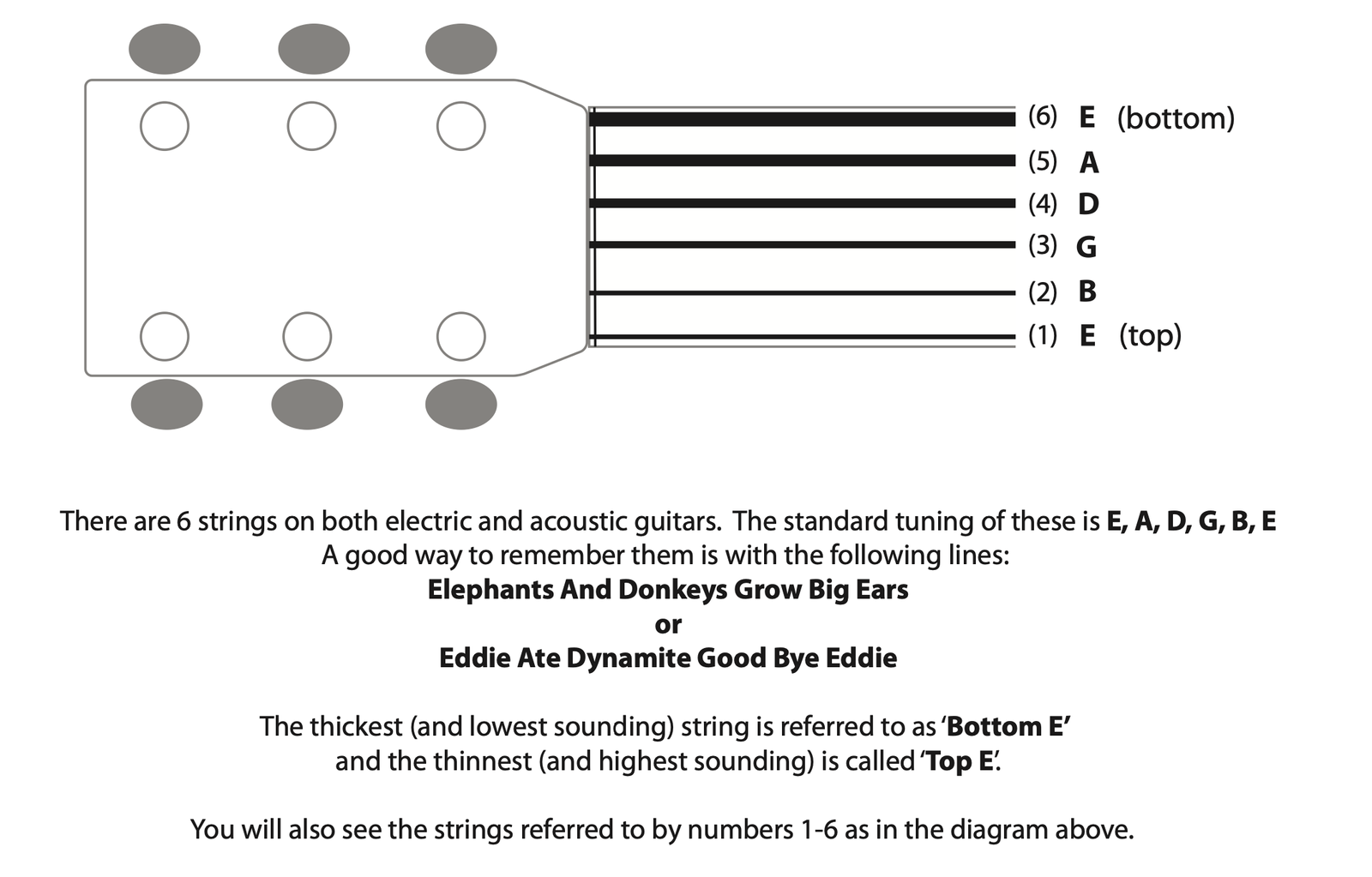
If you have a further interest in ear training (which is endlessly useful when playing an instrument) you can learn the 5th fret relative tuning method. This will be a real foundational asset to learning your guitar.
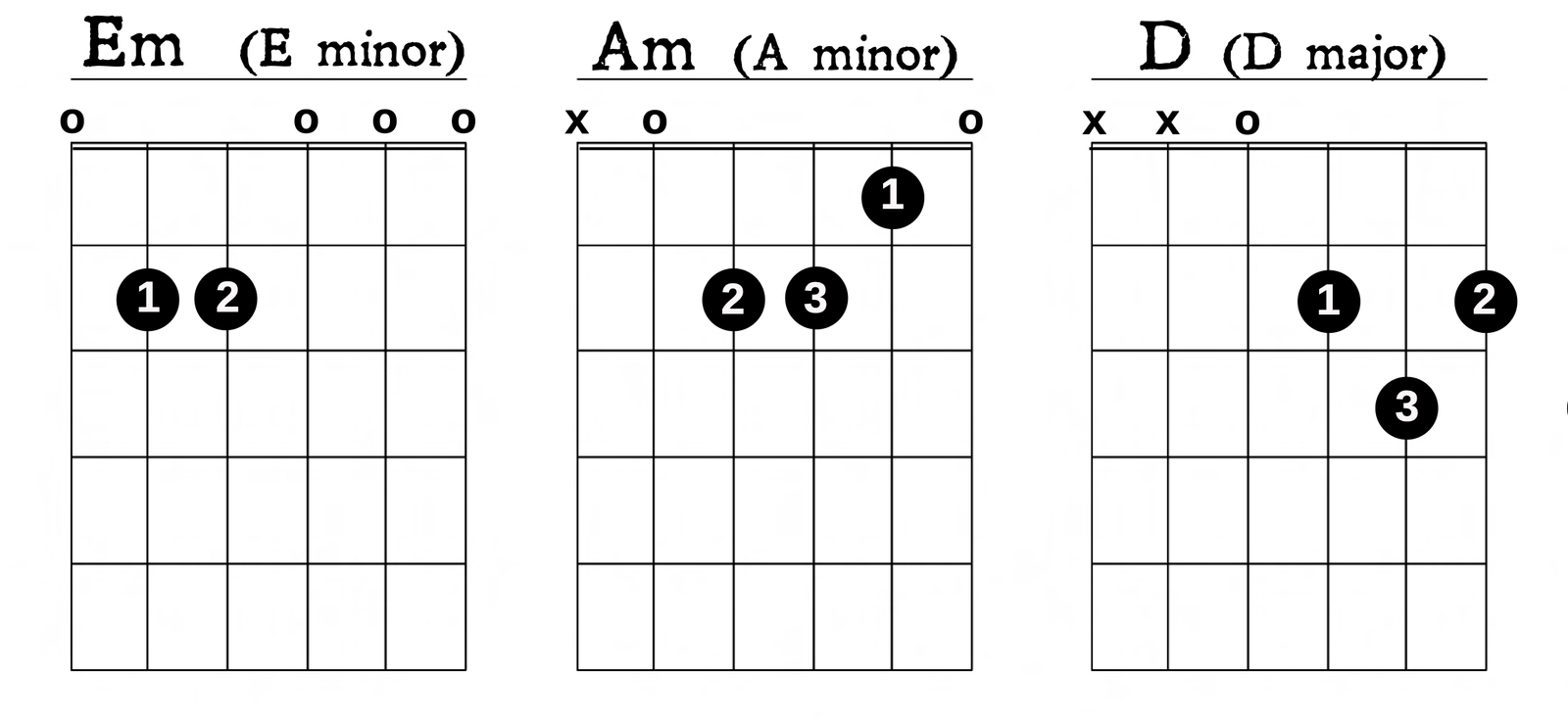
Learning Basic Chords
Chords are one of the foundations of music. Start by learning a few simple open chords like Em, E, A, Am, D, Dm, G and C. These are 8 of the most common chords in guitar playing. Even with Em, A and D you will be able to start learning some songs. Focus on learning 2 or 3 chords at once. Learn the names and the shapes and practise switching between them smoothly. Once you know them add another 3 chords into the mix and build up your chord palette a bit at a time.
Chords are written down on diagrams called chord boxes. Understanding how to read a chord box is an important skill to develop.
Strumming Patterns
Once you’ve mastered some chords, it’s time to learn basic strumming patterns. Start with simple down strokes. Count 1 2 3 4 and play a down stroke on your guitar with each number. Repeat this.
Practice Regularly
Consistent practice is key to improving your guitar skills. Set aside time each day to practise, even if it’s just for a short period.
Remember, learning to play the guitar takes time and patience. Don’t get discouraged if you encounter challenges. Enjoy the process and celebrate your progress!
Would you like to learn more about a specific topic, such as guitar scales, strumming techniques, or chord progressions?

0 Comments